1.2 Hand Hygiene

Please note that the term ‘alcohol-based hand rub (ABHR)’ has now been updated to ‘hand rub’. A hand rub (alcohol or non-alcohol based) can be used if it meets the required standards. Please see further information in the hand hygiene products literature review.
Hand hygiene is considered an important practice in reducing the transmission of infectious agents which cause infections.
Hand washing sinks must only be used for hand hygiene and must not be used for the disposal of other liquids. (See Appendix 3 of Pseudomonas Guidance)
Before performing hand hygiene:
- expose forearms (bare below the elbows)
- remove all hand/wrist jewellery* including any embedded jewellery (a single, plain metal finger ring or ring dosimeter (radiation ring) is permitted but should be removed (or manipulated) during hand hygiene). Bracelets or bangles such as the Kara which are worn for religious reasons should be able to be pushed higher up the arm and secured in place to enable effective hand hygiene which includes the wrists
- ensure fingernails are clean, short and that artificial nails or nail products are not worn
- cover all cuts or abrasions with a waterproof dressing
Hand washing should be extended to the forearms if there has been exposure of forearms to blood and/or body fluids.
*For health and safety reasons, Scottish Ambulance Service Special Operations Response Teams (SORT) in high-risk situations require to wear a wristwatch.
To perform hand hygiene
Hand rubs must be available for staff as near to point of care as possible. Where this is not practical, personal hand rub dispensers should be used.
Application of sufficient volume of hand rub to cover all surfaces of the hands is important to ensure effective hand hygiene. Manufacturer’s instruction should be followed for the volume of hand rub required to provide adequate coverage for the hands. In the absence of manufacturers instructions, volumes of approximately 3ml are recommended to ensure full coverage.
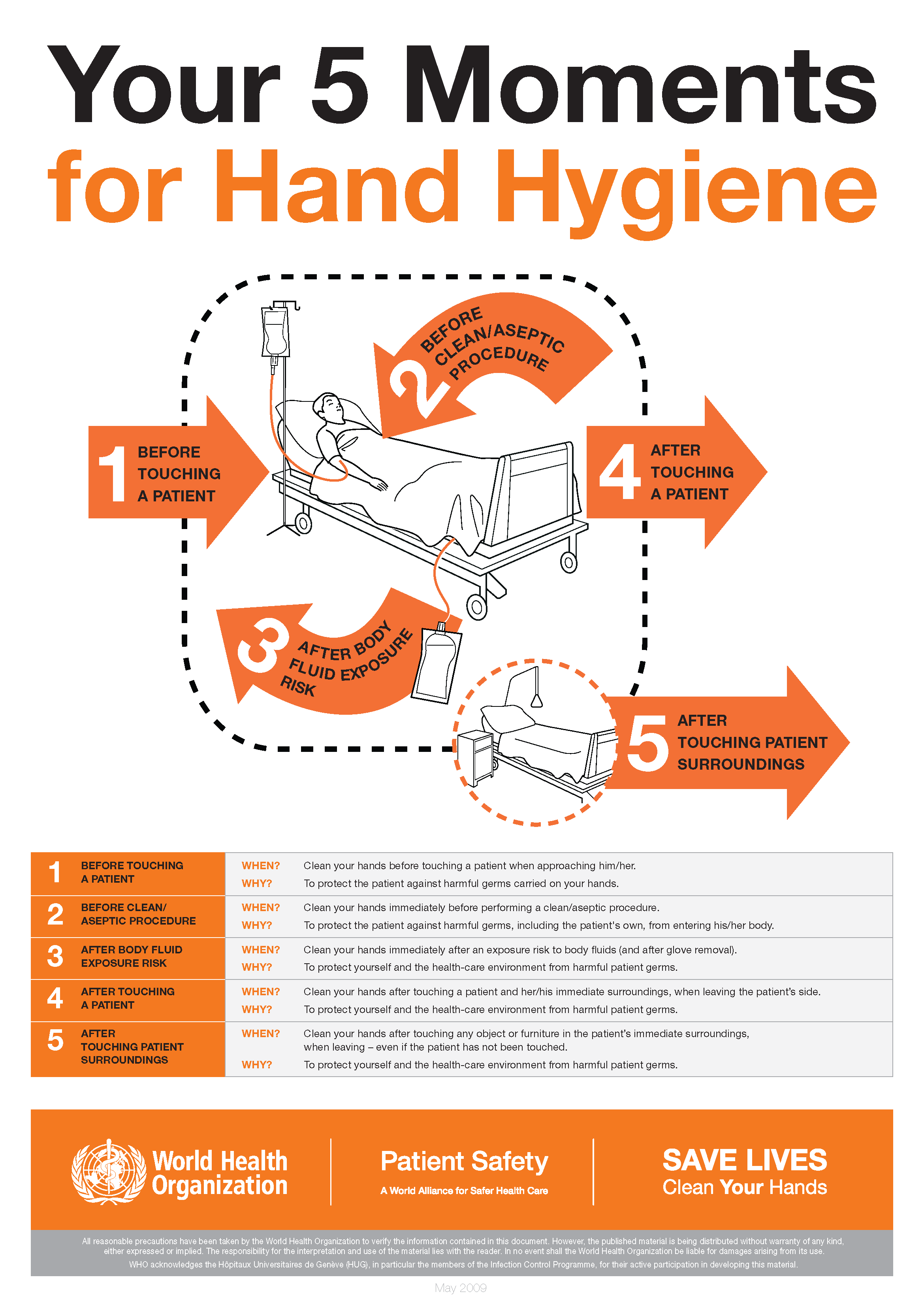
The World Health Organization’s ‘5 moments for hand hygiene’ should be used to highlight the key indications for hand hygiene.
- before touching a patient
- before clean/aseptic procedures. If hand rub cannot be used, then antimicrobial liquid soap should be used
- after body fluid exposure risk
- after touching a patient
- after touching a patient’s immediate surroundings
Some additional examples of hand hygiene moments include but are not limited to:
- before handling medication
- before preparing food
- before donning (putting on) and after doffing (taking off) PPE
- after visiting the toilet
- between carrying out different care activities on the same patient
- after cleaning and disinfection procedures
- after handling waste
Download and print the 5 moments of hand hygiene poster.
Wash hands with non-antimicrobial liquid soap and water if:
- hands are visibly soiled or dirty
- hands are potentially contaminated with blood, other body fluids or excretions
- caring for patients with vomiting or diarrhoeal illnesses
- caring for a patient with a suspected or known gastro-intestinal infection, for example Norovirus or a spore forming organism such as Clostridioides difficile
Hands should be washed with warm/tepid water to mitigate the risk of dermatitis associated with repeated exposures to hot water and to maximise hand washing compliance. Compliance may be compromised where water is too hot or too cold. Hands should be dried thoroughly following hand washing using a soft, absorbent, disposable paper towel from a dispenser which is located close to the sink but beyond the risk of splash contamination.
In all other circumstances use hand rub for routine hand hygiene during care.
Staff working in the community should carry a supply of hand rub to enable them to perform hand hygiene at the appropriate times.
Where staff are required to wash their hands in the service user’s own home they should do so for at least 20 seconds using any hand soap available.
Staff should carry a supply of disposable paper towels for hand drying rather than using hand towels in the individual’s own home. Once hands have been thoroughly dried, hand rub should be used.
The use of antimicrobial hand wipes is only permitted where there is no access to running water. Staff must perform hand hygiene using hand rub immediately after using the hand wipes and perform hand hygiene with soap and water at the first available opportunity.
Resources
(The video above demonstrating Hand Washing and Drying Technique was produced by NHS Ayrshire and Arran)
For how to:
- wash hands see Appendix 1
- hand rub see Appendix 2
Hand hygiene posters and leaflets can be found at Wash Your Hands of Them Resources.
NSS supported WHO World Hand Hygiene Day 2024 - Sharing your knowledge about hand hygiene.
Skin care
- Hand rubs when used for hand hygiene should contain emollients in their formulation.
- Warm/tepid water should be used to reduce the risk of dermatitis. Hot water should be avoided.
- Pat hands dry thoroughly after hand washing using disposable paper towels. Avoid rubbing which may lead to skin irritation/damage.
- Use an emollient hand cream during work and when off duty. These should be applied all over the hands including between the fingers and the back of the hands.
- Do not use refillable dispensers or provide communal tubs of hand cream in the care setting.
- Staff with skin problems should seek advice from occupational health or their GP.
- Barrier creams should not be used in the workplace.
Surgical hand antisepsis
Surgical scrubbing/rubbing applies to persons undertaking surgical and some invasive procedures.
Perform surgical scrubbing/rubbing before donning sterile theatre garments or at other times, for example prior to insertion of central vascular access devices.
Surgical scrubbing using an antimicrobial surgical scrub product should be used for the first surgical hand antisepsis of the day. Or perform hand hygiene using water and a non-antimicrobial liquid soap prior to the first surgical antisepsis of the day, this can be carried out in an adjacent clinical area.
For surgical scrubbing
- Remove all hand/wrist jewellery.
- Nail brushes should not be used for surgical hand antisepsis.
- Nail picks (single-use) can be used if nails are visibly dirty.
- Soft, non-abrasive, sterile (single-use) sponges may be used to apply antimicrobial liquid soap to the skin if licensed for this purpose.
- Use an antimicrobial liquid soap licensed for surgical scrubbing or hand rub licensed for surgical rubbing (as specified on the product label).
- Hand rub can be used between surgical procedures if licensed for this use or between glove changes if hands are not visibly soiled.
- Skin should be blotted dry with sterile single-use towels.
Resources
- For surgical scrubbing technique see Appendix 3.
- For surgical rubbing technique see Appendix 4.
Further information can be found in the Hand Hygiene literature reviews: